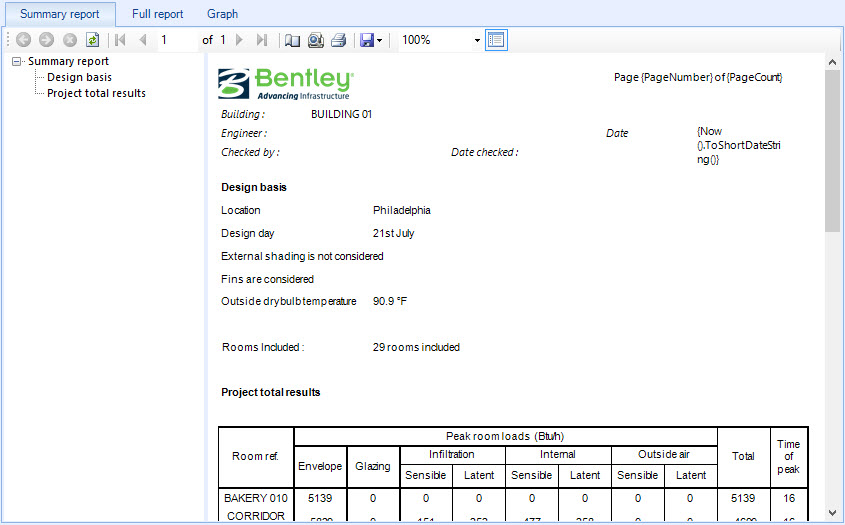
| Design basis
|
Used to display key design parameters considered
for the ASHRAE RTS calculation. Selecting Design basis in the selector panel
(left) updates the reports display panel (right), scrolling to the Design basis
display.
-
Location — Displays the project location set for the project in the Properties
dialog box’s
Properties For: Site
panel.
- Design
Day — Displays the day on which the greatest loads are experienced. The design
day is used to compute sun positions and solar gains and to calculate the
hourly outside dry and wet bulb temperatures using the weather database
information for the specified location.
-
External shading is/is not considered — Indicates external shading is or is not
considered. The use of external shading for gains calculations is set in the Default
Manager dialog box’s
Simulation run-time control
panel. If you opt to include external shading, the
calculation will check if each window is shaded by external obstructions at
each hour of the day. Shaded windows will receive diffuse solar radiation only.
- Fins
are/are not considered — Indicates fins are or are not considered. The use of
external shading for gains calculations is set in the Default
Manager dialog box’s
Simulation run-time control
panel.
-
Outside drybulb temperature — Displays the maximum outside drybulb temperature
experienced on the design day. This value comes from the weather profile being
used for the project.
- Rooms
included — Displays the number of rooms included in the calculation.
|
| Summary results
|
Summary results give a single line summary for each
room showing the peak temperature and time of peak for the room. The data is
arranged in the following table:
- Room
ref. — Displays the name of each project room.
- No.
off — Displays a room multiplier value. A room multiplier is used in computing
project totals. This enables you to set up typical rooms of which there may be
say twenty of one room type, eight of another, etc. Make sure that rooms you
treat in this way are identical, including orientation. Rooms can be placed in
particular zones and floors so that zone and floor sub-totals can be selected
and computed if required.
- Peak
room loads — Several columns display the total loads at the peak hour of the
design day. Each column displays one of the component loads that, when added
together, make up the total load. They are:
-
Envelope – Heat flow through each exposed wall is computed from the wall area,
U value, cooling and load temperature differences. The temperature difference
value is automatically included in the calculation, and a correction is made
for wall color, inside temperature and average outside temperature. The wall
color correction is carried out using the wall absorption coefficient to solar
radiation.
-
Glazing – For each window, the maximum solar gain on the sunlit portion is
determined, and the actual sunlit and shaded areas of glass are computed from
the window dimensions and the side and top projection distances. Cooling load
factors for each hour of the day are applied, depending on whether interior
shading is specified or not. The shading coefficient is incorporated for all
window types. For the glass in the shade, the wall cooling load factor for
north facing, shaded walls is used. The thermal weight used is that specified
for the room. Orientations are rationalized from angles to the nearest ASHRAE
orientation (N, NNE, NE, etc). Rooflights are treated in exactly the same way
as windows, except that they are assumed to be unshaded and subjected to
radiation for a horizontal surface.
-
Infiltration – The infiltration heat gain is found from the room volume, the
infiltration air change rate, and the inside and outside temperatures.
Infiltration gains are separated into their sensible and latent components.
-
Internal – Gains from internal sources are determined. Internal gains are
separated into their sensible and latent components.
-
Outside Air – Outside air may be introduced locally to rooms, in which case it
will affect the room load. Outside air from the central plant will form part of
the supply air and will be a load on the central plant as well. Conditioned
primary air will be supplied at the defined supply temperature, with optional
supply humidity control. Conditioned primary air will affect both room loads
and central plant loads. If conditioned primary fresh air is specified and this
fresh air requires heating at the central plant, when the building requires
cooling (or vice versa), then the fresh air heat load will be excluded from the
central plant loads.
- Total —
Displays the sum of all the peak room loads (on the design day) for each room.
- Time
of Peak — Displays the hour in which the greatest loads are experienced for
each room.
|